FPGA Board for Beginner
FPGA for Beginners
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturing – hence the term “field-programmable”.
The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware description language (HDL), similar to that used for an Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC). Circuit diagrams were previously used to specify the configuration, but this is increasingly rare due to the advent of electronic design automation tools.

FII was founded on making FPGA technology more approachable for students or FPGA beginners to learn. We partnered with the world leader and founder of modern day FPGA technology, Altera and Xilinx, to create platforms that were ideally suited for learning.
Below are boards that we recommend for beginning users. These boards have course material, books, and tutorials to get you started!
Altera FPGA Study Board, JTag downloader, Verilog for beginner – Cyclone-10 FPGA Development Board – $59
Altera FPGA Study Board, JTag downloader, Verilog for beginner – Cyclone-10 FPGA Development Board – $69 (FPGA Type: 10CL010 )
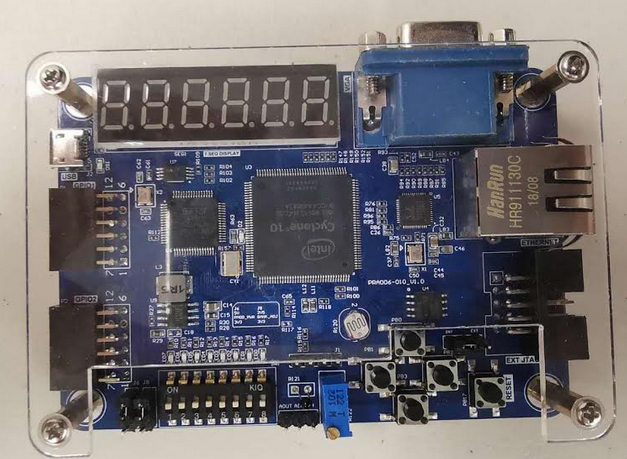
The advantage of FPGA beginner study board:
- Beginner FPGA study board, cheaper but fully functional. cellphone sized. ( < 80 USD )
- power supply and download at the same time, no extra power supply and no extra data transfer line needed
- Small volume and light and can be put into your pocket. size: 10cm X 7 cm.
- Unique function: can be a study board as well a multifunctional JTAG downloader.
- We use newest version Intel FPGA within two years and you can always keep in the front of FPGA industry.
- I2C,UART,UD/DA supported

FII-PRA006 is both a FPGA development board and a JTAG down-loader. As a JTAG down-loader, It support:
- Intel(Altera) FPGA:Support Quartus II5.0 and all the version afterwords;
- Xilinx FPGA:Support ISE9.0 and all version afterwords or All Vivado versions;
- Compatible with ARM Cortext:Support OpenOCD
- RISC-V CPU:Support FreeDomStudio,including GCC、OpenOCD、and GDB Debugging
Altera FPGA Study Board Hardware Resources:
- 6 seven_seg_r
- VGA Video Interface × 1
- 1G Ethernet Interface × 1
- I2C EEPROM × 1
- DIP Switch × 8
- Controllable LED light × 8
- Photoresistance × 1
- Thermistor × 1
- Adjustable Varistor × 1
- Buttons × 4
- GPIO Interface × 2
- Micro usb Interface(Power Supply and downlaod ) × 1
- SPI Communication Interface × 1
- AD/DA Conversion chip × 1
- JTAG Download Interface × 1
- FLASH 32Mbit × 1
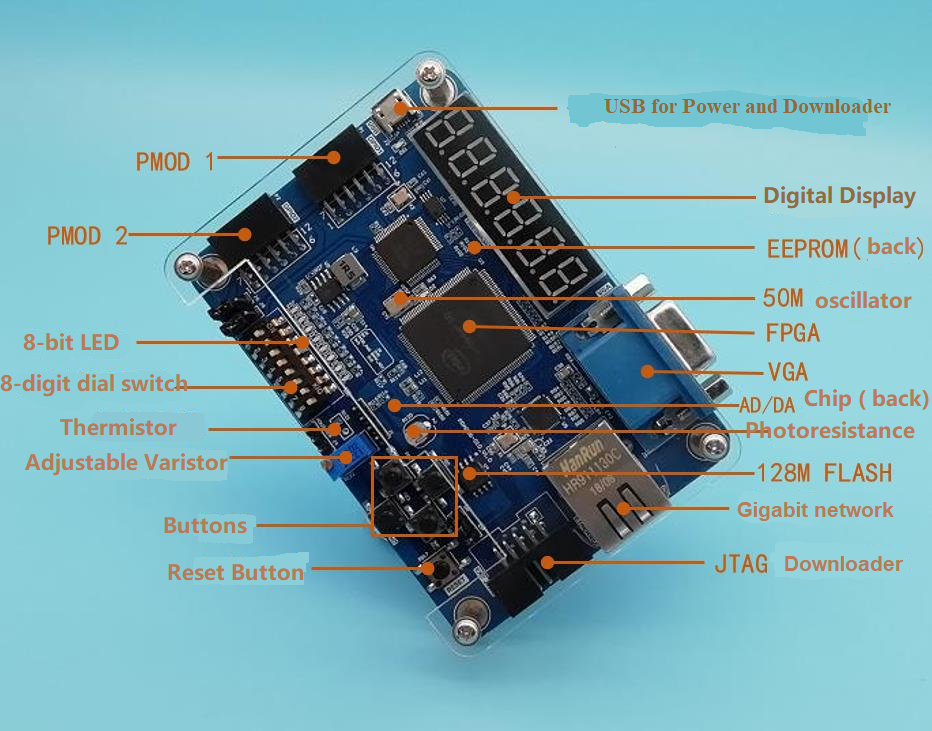
The Biggest Hardware Benefits:
-
- USB port for power supply, downloader, communications ;
- One 50M Oscillator. A stable clock for development board;
- 6-digit common anode digital tube,display the data by dynamic scan;
- 1 VGA port to display picture and video;
- 1 I2C port EEPROM chip,Model: AT24C02;
- 1 adaptive 10M, 100M/1000M Ethernet port;
- 5 buttons,4 for programmable buttons , and one button for resetting;
- 1 Photoresistance. It can be used for simulating light control;
- 1 thermistor. It can be used for collecting temperature or simulating alarm function
- An adjustable resistor can simulate voltage changes, etc.
- 1 PCF8591 AD/DA Conversion chip;
- 8-digit dial switch;
- 8-bit LED light-emitting diode;
- One 128Mbit Flash Chip;
- 2 GPIO external port for communication extension port ;
- One JTAGPort , and make PRA006/010 a functional JTAG down-loader, can be used as a JTAG downloader for Intel,Xilinx and other FPGA downloadable program;
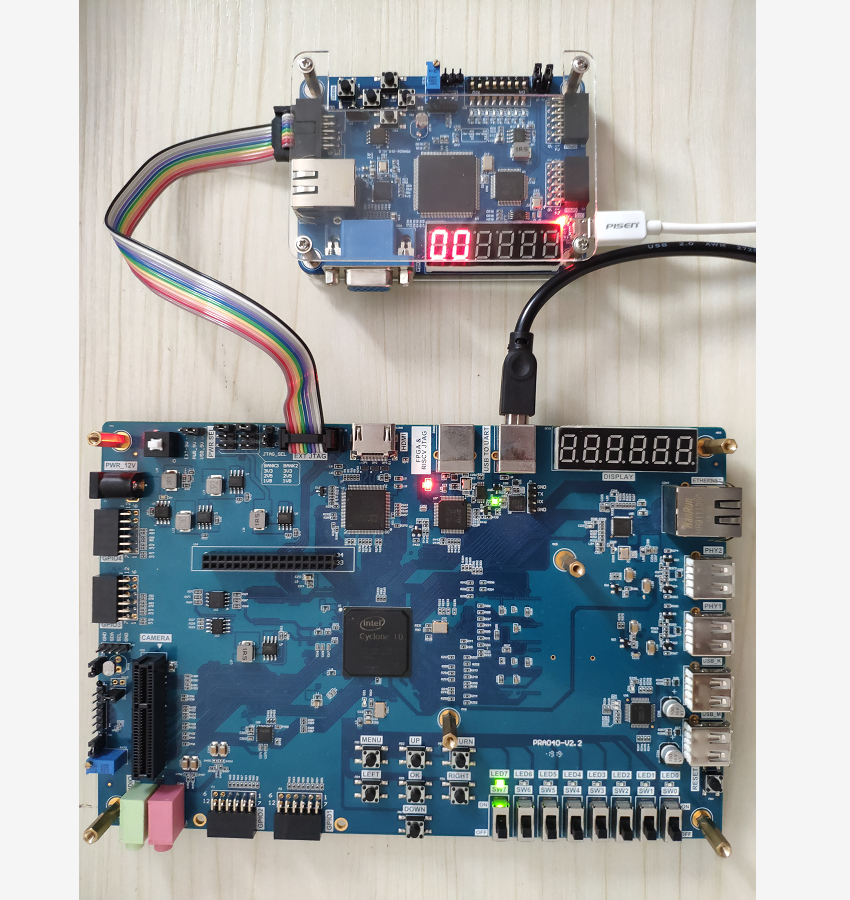
It can also be used with other FPGA development Boards:



Official Shopping Websites
https://fpgamarketing.com/Altera-FPGA-Study-Board-Verilog-for-beginner-Cyclone-10-FPGA-FII-PRA006.htm
FPGA for Beginner Tutorial – FPGA Experimental Manuals
-
-
- FPGA Board for beginner – FII-PRA006/010 Hardware Reference Guide
- LED_shifting , Frequency Divider Verilog HDL Code using the development software Quartus, FPGA pin assignment – FPGA Board Beginner Tutorial – FII-PRA006 Experiment 1
- Switch and Use SignalTap II Logic Analyzer in Quartus ( Verilog HDL code ), Learn to analyze the captured signals – FPGA for Beginner Tutorial – Experiment 2 – FII-PRA006
- BCD_counter, The segment decoder code, Download the program into the board flash memory – FPGA for Beginner Tutorial – Experiment 3 – FII-PRA006
- Building new FPGA projects in Quartus, device selection, PLL setup, PLL frequency setting, Verilog’s tree hierarchy design, and the use of SignalTap II – FPGA Board for Beginner – Experiment 4 -PRA006
- Block_Debouncing Principle and adaptive programming, PCB schematics, and Verilog HDL Code – FBGA Board for beginner FPGA tutorial – Experiment 5
- Learn to Use Multiplier and ModelSim to Output- FPGA Board for Beginner – FPGA Tutorial – Experiment 6
- Hexadecimal Numbers to BCD Code(hex_to_bcd), binary numbers to BCD code (bin_to_bcd) Conversion and Application – FPGA Board for Beginner Tutorial – Experiment 7
- Design 16 outputs ROM, Study the format of *.mif and how to edit *.mif file to configure the contents of ROM, Use of ROM (Read-only Memory) – FPGA Board for Beginner Tutorial – Experiment 8
- FPGA Tutorial – Use Dual-port RAM to Read and Write Frame Data – FPGA Board for Beginner – Experiment 9
- FPGA Tutorial – Asynchronous Serial Port Design and Experiment – FPGA for Beginner – Experiment 10
- FPGA Beginner Tutorial – IIC Protocol Transmission – FPGA Board for Beginner – Experiment 11
- FPGA Beginner Tutorial – AD, DA Experiment – FPGA Board for Beginner – Experiment 12
- FPGA Beginner Tutorial – VGA Experiment – FPGA Board for Beginner – Experiment 13
- FPGA Beginner Tutorial – Ethernet Experiment – FPGA Board for Beginner – Experiment 14
- The Newest Experimental Version – FPGA for Beginner Board Experimental Manuals and Study Guide – PRA006, PRA010 FPGA Beginner Study Board
-
FPGAs provide benefits to designers of many types of electronic equipment, ranging from IOT, smart homes, smart energy grids, aircraft navigation, automotive driver’s assistance, medical ultrasounds and data center search engines, and so on.
We will send you experimental manuals when you have bought our pocket study board. PRA006 or PRA010
The Benefits of FPGA
Flexibility
- FPGA functionality can change upon every power-up of the device. So, when a design engineer wants to make a change, they can simply download a new configuration file into the device and try out the change.
- Often, changes can be made to the FPGA without making costly PC board changes.
- ASSPs and ASICs have fixed hardware functionality that can’t be changed without great cost and time.
Acceleration
- FPGAs are sold “off the shelf” vs. ASICs (which require manufacturing cycles taking many months).
- Because of FPGA flexibility, OEMs can ship systems as soon as the design is working and tested.
- FPGAs provide off-load and acceleration functions to CPUs, effectively speeding up the entire system performance.
Integration
Today’s FPGAs include on-die processors, transceiver I/O’s at 28 Gbps (or faster), RAM blocks, DSP engines, and more. More functions within the FPGA mean fewer devices on the circuit board, increasing reliability by reducing the number of device failures.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- While ASICs may cost less per unit than an equivalent FPGA, building them requires a non-recurring expense (NRE), expensive software tools, specialized design teams, and long manufacturing cycles.
- Intel FPGAs support long lifecycles (15-years or more), avoiding the cost of redesigning and requalifying OEM production equipment if one of the electronic devices on-board goes end of life (EOL).
- FPGAs reduce risk, allowing prototype systems to ship to customers for field trials, while still providing the ability to make changes quickly before ramping to volume production.
The concept behind an FPGA’s programmability is a basic building block containing various logic types that are connected and interconnected to perform any logic function. “Basic building block” is a generic term that I’m using, but you may hear terms like “logic cells,” “combinational logic blocks” (CLBs), or “logic array blocks” (LABs); it depends on the manufacturer. The basic building block contains logic resources and is the starting point that the FPGA uses to constructs the design.
We will send you following documents after you have bought our products:
The experimental manual of FII-PRA006 and FII-PRA010 pocket Board for beginners
The Hardware Configuration of FII-PRA006 and FII-PRA010 Board for beginners
The Schematic Diagram of FII-PRA006 and FII-PRA010 FPGA Board for beginners

We will send you above documents after you have bought our PRA006 pocket study board.
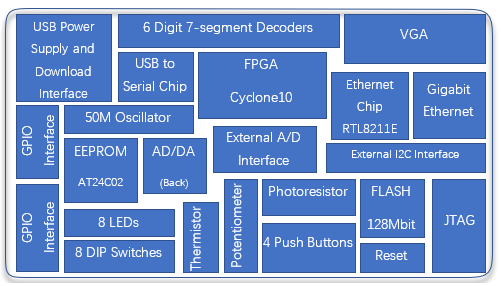
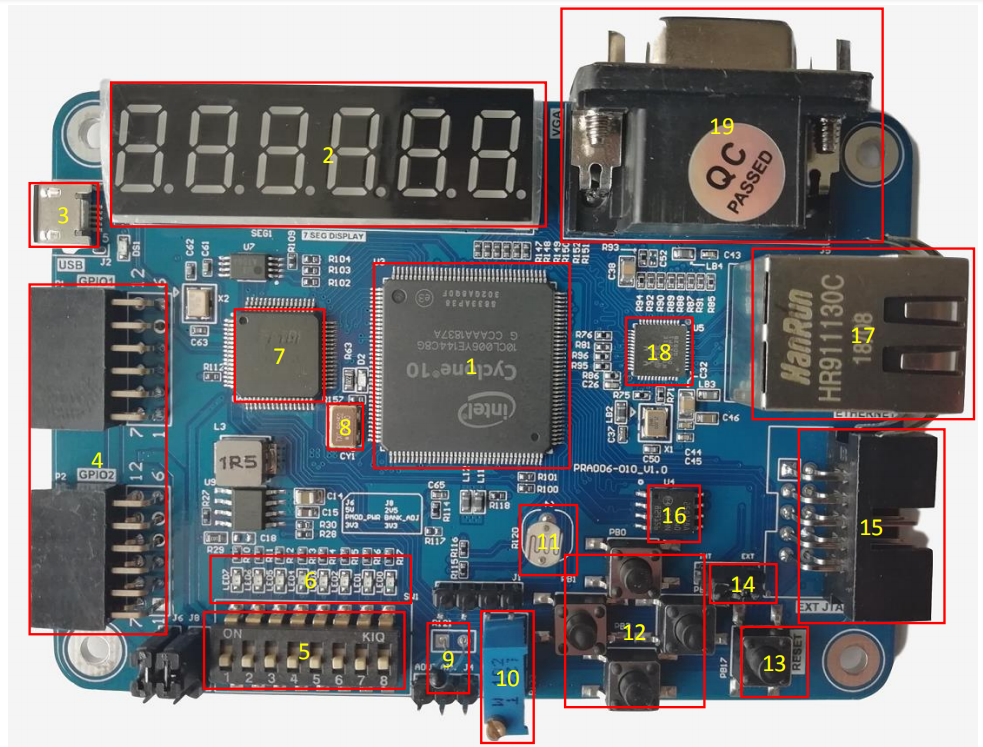
What is the main components of the FRA006 FPGA beginner board ?
-
- 10CL006YE144C8G or 10CL006YE144C8G
- 6-digit common anode seven-segment display
- USB power supply and download interface
- External expansion interface GPIO
- 8 DIP switches
- 8 LEDs
- USB to serial port chip (FT2232)(Intefrated JTAG download function)
- 50 MHz oscillator
- Thermistor (NTC-MF52)
- Potentiometer
- Photoresistor
- 4 buttons (up, down, right, down)
- Reset button (Reset)
- JTAG downloader function conversion interface
- JTAG download interface (Used only when the board is used as a downloader)
- Flash (N25Q128A, 128M bit/16M bytes)
- Ethernet interface
- Ethernet PHY chip (RTL8211E-VB)
- VGA interface
- Back of the board U8: AD/DA conversion chip (PCF8591)
- Back of the board U13: EEPROM (AT24C02N)
Extension Experiments
Video Camera
- Pictures and Videos Collection
- Edge check and human-face location Positioning
- Picture and video Zip and UnZip
Voice and Speech
- voice and speech collection
- Speech Recognition
- High Speed Analog signal acquisition
Risc-V
- Low level CPU programing
- Run C language
- C language debugging onboard device